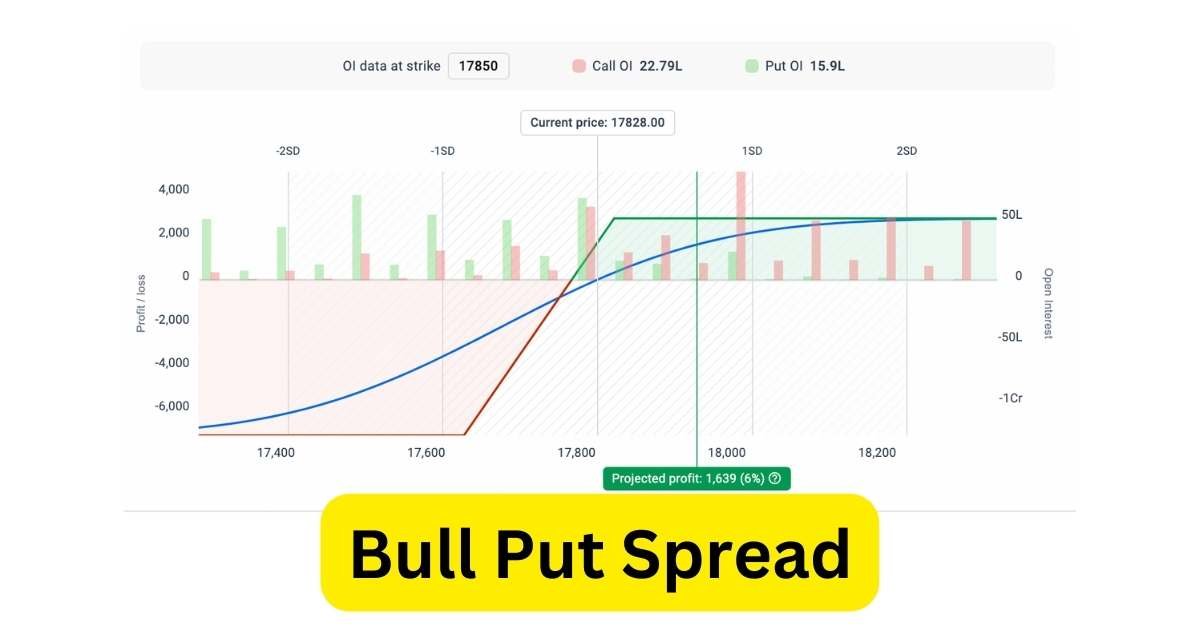
What is a Bull Put Spread Option Strategy?
Bull Put Spread Option Strategy is a popular options trading strategy used by investors and traders who have a bullish outlook on a particular stock or index. It is a type of credit spread where the trader sells a put option with a lower strike price and buys a put option with a higher strike price, simultaneously. The primary goal of this strategy is to earn a net credit by collecting the premium from the sold put option, which reduces the overall cost of buying the long put option.
In this article, we will get into the mechanics of a bull call spread, its Uses, advantages and disadvantages, risks, examples, and some key considerations when implementing this strategy.
When to execute a Bull Put Spread Option Strategy?
A bull put spread option strategy is typically executed when an investor or trader is moderately bullish on a stock or options or other underlying assets. This strategy involves selling a put option with a higher strike price while simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price. The goal is to profit from a bullish move in the underlying asset while limiting potential losses.
Here are some scenarios where a bull put spread option strategy might be appropriate:
- When an investor expects the price of an underlying asset to increase moderately in the near future.
- When an investor wants to generate income by collecting premiums from selling put options while limiting their downside risk.
- When an investor wants to offset the cost of buying a long call option with the premiums collected from selling put options.
It is important to note that this strategy has limited profit potential and limited risk, so it may not be suitable for all investors or market conditions. It is always recommended to thoroughly understand the risks and rewards associated with any investment strategy before executing it.
How Does a Bull Call Spread Option Strategy Work?
The bull put spread is an options strategy that involves selling a put option with a higher strike price while simultaneously buying a put option with a lower strike price. The two options should expire at the same time.
Here are the mechanics of a bull put spread:
- Choose the underlying asset: The first step in implementing a bull put spread is to select an underlying asset. This could be a stock, ETF, or index.
- Determine the expiration date: Next, you need to choose an expiration date for the options. Both options should expire at the same time.
- Select the strike prices: Choose a strike price for the put option you will sell and another for the put option you will buy. The strike price of the sold put option should be higher than the strike price of the bought put option.
- Sell the put option: Sell the put option with the higher strike price to generate income from the premium.
- Buy the put option: Buy the put option with the lower strike price to limit your risk if the underlying asset price drops.
- Manage the position: Once the trade is executed, monitor the position regularly. If the underlying asset price increases, the bull put spread will make a profit. If the underlying asset price decreases, the maximum loss is limited to the difference between the strike prices minus the premium received.
The bull put spread is a limited risk, limited reward strategy that can be used when an investor is moderately bullish on an underlying asset. It can generate income and limit losses if the market moves against the investor. However, as with any investment strategy, it is important to understand the risks and rewards and to manage the position appropriately.
How to trade a Bull Put Option Strategy | Example of Bull Put Spread Option Strategy
Assume that a trader is bullish on a particular stock, HDFC, which is currently trading at 100 Rs per share. The trader believes that the stock will continue to rise or, at the very least, remain above a certain price level.
The trader decides to implement a Bull Put Spread strategy to profit from the expected bullish move while limiting the potential downside risk. Here’s how the strategy would work:
- Sell a Put Option with a Lower Strike Price: The trader sells a put option with a strike price of 95 Rs, expiring in two months, for a premium of 2 Rs per share. This option gives the buyer the right to sell the stock to the trader at the 95 Rs strike price, but only before the expiration date.
- Buy a Put Option with a Higher Strike Price: The trader buys a put option with a strike price of 90 Rs, expiring in two months, for a premium of 0.50 Rs per share. This option gives the trader the right to sell the stock to the counterparty at the 90 Rs strike price, but only before the expiration date.
The net premium received by the trader is 1.50 Rs per share (2 Rs premium received for selling the put option minus the $0.50 premium paid for buying the put option). The total potential profit is limited to the net credit received, which is 150 Rs (1.50 Rs x 100 shares per contract).
The maximum potential loss is the difference between the strike prices (95 – 90 = 5 Rs) minus the net credit received (1.50 Rs), which is 3.50 Rs per share or 350 Rs for the entire contract. This loss would occur if the stock price were to fall below 90 Rs at expiration, and both put options were exercised.
However, the trader has limited the potential downside risk by owning the long put option with a higher strike price, which provides protection against a decline in the stock price. If the stock price were to fall below the 90 Rs strike price, the long put option would gain value, offsetting the losses from the short put option.
If the stock price were to remain above the 95 Rs strike price at expiration, the trader would earn the net credit received of 1.50 Rs per share, or 150 Rs for the entire contract. The trader can also close the position before expiration by buying back the short put option and selling the long put option to lock in profits or minimize losses.
The Bull Put Spread strategy offers limited risk and limited reward opportunities for traders who are bullish on a particular stock or index. It provides a cushion against a downward move in the underlying asset while allowing traders to profit from a bullish move with a lower capital requirement compared to buying the underlying asset outright. However, as with any options strategy, it is important to understand the potential risks and manage them accordingly.
When to exit from Bull Put Spread ?
When using a bull put spread, it’s important to have an exit strategy in place to manage risk and lock in profits. Here are a few potential exit strategies:
- Close the spread early: If the underlying asset moves up quickly, it may be possible to close the spread early for a profit. This involves buying back the short put option and selling the long put option, which eliminates the risk of the trade and locks in any profits.
- Let the spread expire: If the underlying asset remains above the strike price of the short put option at expiration, the option will expire worthless and the trader will keep the premium. This is a successful outcome for the trade.
- Adjust the spread: If the underlying asset starts to move against the position, it may be possible to adjust the spread by rolling the short put option up to a higher strike price or by adding a long put option with a higher strike price. This can limit losses and provide more upside potential.
The key to successful options trading is to have a well-defined strategy with clear entry and exit rules. A bull put spread can be a profitable strategy if executed correctly and managed effectively.
What are the advantages of the Bull Put Spread Option Strategy?
The Bull Put Spread option strategy can offer several advantages to traders. Here are some of the advantages of the Bull Put Spread:
- Limited risk: The Bull Put Spread is a limited-risk strategy, which means that the maximum loss that a trader can incur is limited to the difference between the strike prices of the put options minus the net credit received when entering the trade.
- Defined reward: The Bull Put Spread also offers a defined reward, which is limited to the net credit received when entering the trade. This can help traders to manage their risk-reward ratio more effectively.
- Profit in a bullish market: The Bull Put Spread is a bullish options strategy, which means that it can be profitable in a rising market. Traders can profit from the upward price movement of the underlying asset while limiting their risk.
- High probability of success: The Bull Put Spread has a high probability of success because it involves selling an out-of-the-money put option, which means that the underlying asset would have to decline significantly for the trade to be unprofitable.
- Versatile strategy: The Bull Put Spread is a versatile strategy that can be used in a variety of market conditions. It can be used to generate income, hedge against downside risk, or as a standalone bullish trade.
Basically, the Bull Put Spread option strategy can offer traders limited risk, defined reward, and a high probability of success.
What are the disadvantages of the Bull Put Spread Options Strategy?
While the Bull Put Spread Option Strategy is a popular and potentially profitable options strategy, there are also some disadvantages and risks associated with it. Here are some of the disadvantages of the Bull Put Spread:
- Limited profit potential: The maximum profit potential of the Bull Put Spread is limited to the net credit received when entering the trade. This means that if the underlying asset price rises significantly, the trader will only capture a portion of the upside potential.
- Margin requirements: When entering a Bull Put Spread trade, traders are required to post the margin in order to secure the short put option. Depending on the broker and the underlying asset, the margin requirement for a Bull Put Spread can be significant.
- Potential for early assignment: The short put option in a Bull Put Spread can be assigned early if the option is in the money. This can lead to unexpected losses or additional transaction costs.
- Market risk: Like all options strategies, the Bull Put Spread is subject to market risk. If the underlying asset price declines significantly, the trade can result in a loss.
- Limited flexibility: Once a Bull Put Spread trade is entered, it can be difficult to adjust or exit the trade before expiration. This can limit a trader’s flexibility and ability to manage risk.
The Bull Put Spread can be a profitable options strategy, but traders should be aware of the potential risks and disadvantages before entering the trade. It is important to have a solid understanding of the strategy and to carefully manage risk to minimize potential losses.
What are the things to consider before applying a Bull Put Spread Options Strategy?
Before applying a Bull Put Spread options strategy, traders should consider several key factors to determine whether the trade is appropriate for their investment objectives and risk tolerance. Here are some of the things to consider:
- Market outlook: The Bull Put Spread is a bullish options strategy, so traders should have a positive outlook on the underlying asset in order to use this strategy effectively. It’s important to consider factors such as market trends, economic indicators, and company fundamentals to assess the potential for price appreciation.
- Option pricing: Traders should carefully evaluate the pricing of the put options they plan to use in the Bull Put Spread. The goal is to sell an out-of-the-money put option to generate income, but the premium received should be high enough to compensate for the risk involved.
- Strike prices: The selection of strike prices is a critical component of the Bull Put Spread. Traders should choose a short put option strike price that is below the current market price and an long put option strike price that is further below the short put option strike price. This can help to limit the potential loss and maximize the profit potential of the trade.
- Risk management: It’s important to have a plan in place for managing risk in the Bull Put Spread. This can include setting stop-loss orders, adjusting the position as needed, and diversifying the portfolio to minimize overall risk.
- Margin requirements: Traders should be aware of the margin requirements associated with the Bull Put Spread. Depending on the broker and the underlying asset, the margin requirement for this strategy can be significant.
Traders should carefully evaluate their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and market outlook before applying a Bull Put Spread options strategy. By considering these key factors and implementing effective risk management techniques, traders can potentially generate income and manage risk using this popular options strategy.
What are the risks involved in Bull Put Spread Option Strategy?
While the Bull Put Spread options strategy can be a profitable strategy, there are several risks involved that traders should be aware of. Here are some of the main risks associated with the Bull Put Spread Option Strategy:
- Market risk: Like all options strategies, the Bull Put Spread is subject to market risk. If the underlying asset price declines significantly, the trade can result in a loss. It’s important to have a solid understanding of the underlying asset and to carefully monitor market conditions.
- Assignment risk: The short put option in a Bull Put Spread can be assigned early if the option is in the money. This can lead to unexpected losses or additional transaction costs. Traders should be prepared for the possibility of early assignment and have a plan in place to manage the risk.
- Margin risk: When entering a Bull Put Spread trade, traders are required to post margin in order to secure the short put option. Depending on the broker and the underlying asset, the margin requirement for a Bull Put Spread can be significant. Traders should be aware of the margin requirements and have sufficient funds available to meet them.
- Limited profit potential: The maximum profit potential of the Bull Put Spread is limited to the net credit received when entering the trade. This means that if the underlying asset price rises significantly, the trader will only capture a portion of the upside potential.
- Early exit risk: Once a Bull Put Spread trade is entered, it can be difficult to adjust or exit the trade before expiration. This can limit a trader’s flexibility and ability to manage risk.
Overall, traders should carefully evaluate the risks associated with the Bull Put Spread and have a solid understanding of the strategy before entering the trade. By implementing effective risk management techniques and monitoring market conditions, traders can potentially generate income and manage risk using this popular options strategy.